The Texas Solar Energy Revolution Is Going Global
time:2024-02-20 10:41:59 Views:0 author:Jinan Freakin Power Ltd.
The solar energy industry of Texas is in a weird situation politically, but that doesn’t seem to stop investors from pumping more green gold into the state’s economy. The latest news is particularly interesting because it illustrates how manufacturers based in other states — and other countries — can leverage renewable energy projects in Texas to turbo-boost their clean power profiles.

If you guessed South Carolina is one of those other states, run right out and buy yourself a cigar. Currently, South Carolina places a respectable #14 in a 50-state ranking of installed solar capacity. However, according to records compiled by the Solar Energy Industries Association the state earns a less respectable #22 slot for five-year projected growth in solar capacity. That’s not good news for electric vehicle manufacturers and other clean tech companies that hope to burnish their green cred by decarbonizing their factories. Fortunately, solar-hungry businesses don’t have to wait for the South Carolina solar pot to boil. They can get credit for new solar projects in other states, by investing in Renewable Energy Certificates. Despite some concerns over transparency in the REC market, the Rocky Mountain Institute is among the renewable energy advocates that count on RECs to help foster rapid decarbonization, To address the transparency objections, RMI is developing a more rigorous, quantitative approach to measuring the impact of RECs.
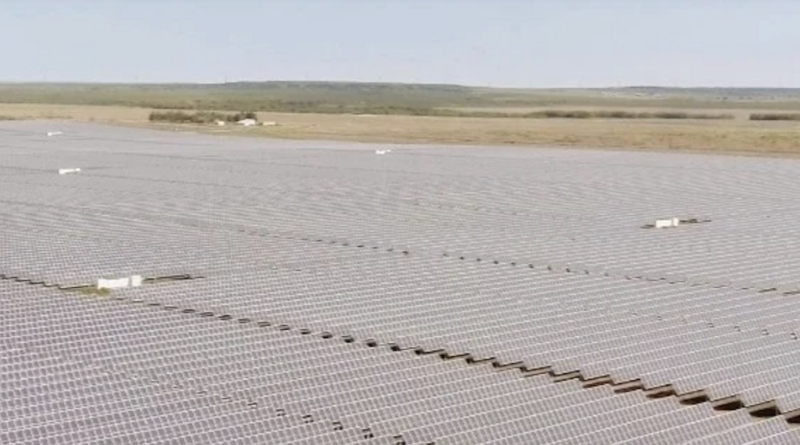
Texas has acquired a powerful solar energy profile, so it’s difficult for one project to stand out, but Misae II is one of them. The power purchase agreement with JNA will help finance the initial 319-megawatt (DC) stage of the project. The solar array will reach 695 megawatts when fully built out, making it one of the biggest solar energy projects in Texas and the entire US, too. While JNA can’t directly use the electricity from its share of 142.8 megawatts, its share of Misae II represents the equivalent of all the electricity consumption at the company’s North American production facilities, offsetting about 124,600 tons of carbon annually.